Updated for 2025
This post was originally published in June 2020 and has been updated to reflect the significant changes in cloud computing, serverless architecture, and AI integration over the past five years.
The Cloud is Complex
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has become even larger in 2025 than it was five years ago, despite the sunsetting of some services, including WorkDocs. Beyond the traditional challenge of creating servers in EC2 and managing static content in S3, AWS offers over 250 services spanning compute, storage, AI/ML, generative AI, IoT, and industry-specific solutions. New services and features appear pretty often, though the pace of non-AI products may have slowed in recent months.
And expanding on AI is where the action is for AWS, which is not unlike the other cloud providers. Services like Amazon Bedrock for foundation models and SageMaker's continued evolution with the new Sagemaker AI (the next generation, according to AWS) have fundamentally changed what's possible in the cloud. AWS is no longer just infrastructure—it's a platform for building intelligent applications. In many cases, organizations are not looking simply for an AWS Serverless Stack, but an AWS AI Stack.
There are so many AWS products that Amazon can't fit them onto a single page. Even broken up into categories, many of the 250+ services aren't easy to find.
(an old view of AWS Products from 2020)
AWS is too large for any one person to fully understand. There are too many features and services, and while the AWS Well-Architected Framework provides high-level guidance, there are best practices and looming pitfalls for most of what you can find.
There are usually multiple solutions to each architectural problem, and it is not always easy to know which solution is the best. And today's best choice may not be the best choice in six months, whether that's due to your use case evolving or the continuing progress in cloud computing.
Serverless Has Matured
Since 2020, when the first version of this post was written, serverless has evolved from an emerging concept to a production-standard approach used at least in part by 70% of AWS customers (at least according to Datadog back in 2023).
What started with AWS Lambda and its functions-as-a-service has expanded into a comprehensive ecosystem:
Modern Serverless Components:
- Lambda has gained ARM-based Graviton processors, container image support, and function URLs
- EventBridge provides sophisticated event routing across services and accounts
- DynamoDB offers enhanced global tables and improved performance
- API Gateway includes better WebSocket support and enhanced authorization
- OpenSearch Serverless eliminates the need to manage search infrastructure—FormKiQ now offers this option for customers who want a solution that is 100% serverless
- S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval provides cost-effective storage for documents with predictable lifecycle patterns
- Step Functions handles complex workflows with enhanced integrations
- Aurora Serverless v2 scales with fine-grained capacity adjustments
What many traditional small web applications look like, a pile of servers. Usually overkill (over-resourced), sometimes not enough to keep things running when usage grows.
(icon by http://www.freepik.com/)
Serverless, at its core, is not just abstracting servers away so you no longer need to care what server is running your workload; it's about removing operational overhead entirely. Instead of lift-and-shift, organizations are re-architecting around event-driven patterns, microservices, and consumption-based pricing models that scale automatically with demand.
We're not living in a zero-ops world yet, but an architecture built on serverless components and managed services is the closest we've ever come.
LLMs as Business Tools
Large Language Models have become integrated into business workflows since the first small steps in late 2022, creating new architectural requirements:
LLM-integrated applications often expose their capabilities through APIs, enabling seamless integration with other services. These APIs can use solutions like API Gateway or Lambda Function URLs to connect backend services, support custom domains, and facilitate integration with CloudFront for greater flexibility and streaming support.
This means that organizations must consider not only the choice of model provider and scaling strategy, but also how to manage variable traffic patterns and unpredictable usage spikes. The architecture must also handle a variety of response types from APIs, including streaming and real-time responses, to support LLM workloads.
New Capabilities to Support:
- Vector storage for semantic search and knowledge retrieval; Amazon S3 Vectors is a new option, but it's still being determined how it compares to other solutions
- Model orchestration across multiple foundation models and providers, with a focus on keeping each app's data separate to ensure privacy and security
- Prompt management and versioning systems
- Embedding pipelines for document processing
- Real-time inference endpoints with variable demand, enabled by services like AWS Bedrock for scalable, serverless AI inference
- Token usage optimization across API calls
- Context management for maintaining conversation state
Traditional architectures weren't designed for these workloads. LLM-integrated applications have variable traffic patterns, require connections with multiple model providers, and need flexible scaling to handle unpredictable demand. This is exactly where serverless excels—and where serverless stacks become essential.
Why Serverless Stacks Matter More Than Ever
A serverless stack is a pre-built, Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) architecture that solves a specific workflow or use case. A full stack boilerplate project can accelerate the deployment of serverless stacks by providing a modular, ready-to-use architecture for building complex AI-powered tools and applications. Instead of manually connecting dozens of services, you deploy a tested, optimized pattern that includes:
- Service configurations and connections (these configurations are created to address specific use cases and workflows)
- Security and IAM policies
- Monitoring and observability
- Cost optimization settings
- Scaling configurations
- Error handling and retry logic
Common Use Cases, Now Better with Serverless
Traditional workflows have become more efficient with mature serverless implementations. Serverless stacks simplify the deployment and management of both backend and frontend components of an app, making it easier to build, deploy, and scale applications. Hosting static assets and web frontends is streamlined using serverless services like S3 and CloudFront, allowing you to host your frontend efficiently. Hosting is a key consideration when deploying serverless applications, as it ensures scalability and reliability for both the app and its users.
API Management
Pre-configured API Gateway with Lambda authorizers, rate limiting, and both caching and CloudFront distribution if needed. CloudFront can be used to proxy API Gateway requests, enabling custom domain management and seamless API access. Different authentication methods, such as Lambda Authorizers or custom JWT-based methods, can be implemented for API Gateway to enhance security and flexibility. It is important to verify user credentials or tokens as part of the API management workflow. And rather than requiring autoscaling or manual capacity tweaks now scales automatically with request volume.
Document Processing
Serverless stacks combine S3 and Lambda with processing through machine learning with services such as Textract and Comprehend, to extract and analyze document content. The document processing logic is implemented as a lambda application, enabling modular and scalable workflows. A shared package is often used within the pipeline for authentication or data validation, such as validating JWT tokens. The response from the document processing API can include extracted data, analysis results, or error messages, depending on the outcome of the workflow. Organizations process millions of documents without managing infrastructure, using well-configured workflows to keep results consistent and costs manageable.
Real-Time Data Processing
Kinesis, Lambda, and DynamoDB work together for streaming data analysis and visualization, handling traffic spikes without capacity planning. As it is important to run tests to ensure the reliability and performance of real-time data processing pipelines, at each stage of the workflow you should verify data integrity and processing accuracy to maintain trust in your results. The response from real-time processing can be visualized in dashboards or used for further analysis to gain actionable insights. This tooling can all be implemented using serverless technologies.
Content Delivery
CloudFront, S3, and Lambda@Edge deliver content globally with automatic optimization and security. Hosting static websites and assets is a core use case for these serverless content delivery solutions, ensuring efficient and reliable deployment. Additionally, plugins can be used to automate and enhance the deployment of static content to CloudFront and S3, simplifying workflows and improving functionality. For instance, the FormKiQ website deploys from GitHub to S3 via a GitHub Action, which also invalidates the CloudFront cache.
Emerging Workflows Enabled by LLMs
New capabilities have emerged that benefit from serverless architecture:
Document Intelligence
Stacks that integrate document processing with Amazon Bedrock to extract, analyze, and generate insights from unstructured content, enabling automated classification, summarization, and metadata extraction.
Knowledge Base Integration
Systems that combine vector storage, retrieval mechanisms, and LLM inference to answer questions based on organizational knowledge. This includes various approaches to semantic search and context-aware responses that may evolve significantly as best practices emerge.
Agentic Workflows
Processes where LLMs assist with decision-making within structured workflows—not always autonomous AI making decisions independently, but human-defined workflows that leverage language models for classification, routing, and analysis steps. With proper configuration and validation, these non-deterministic AI models can provide efficiency gains without introducing new kinds of errors.
Multi-Model Orchestration
Request routing across different models within Amazon Bedrock with fallback handling and cost optimization, allowing organizations to choose the right model for each task.
Serverless Economics Have Improved
Serverless pricing has become even more competitive since 2020:
- Lambda offers tiered pricing with significant cost reductions at scale
- DynamoDB on-demand mode provides predictable pricing without capacity planning
- S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval dramatically reduces storage costs for documents with defined lifecycles
- Bedrock offers both on-demand and provisioned throughput for predictable LLM costs
The key to realizing these cost benefits is proper architecture. Organizations that lift-and-shift traditional applications into the cloud and add serverless components around them often find costs higher than expected. The real savings come from re-architecting to take advantage of serverless patterns: event-driven processing, consumption-based scaling, and eliminating idle resources.
When properly architected, serverless stacks that include cost monitoring, intelligent caching, and efficient service integration can reduce operational costs by 60-80% compared to traditional server-based approaches—while simultaneously improving scalability and reliability.
While there are sometimes write-ups about moving workloads back to on-prem servers, the details in those situations will often showcase examples of architecture that could have been better-optimized for serverless and managed services, rather than a retreat from cloud entirely.
The Infrastructure-as-Code Advantage
Modern serverless stacks are built using tools like AWS CDK, Terraform, or the Serverless Framework. This means:
- Version control for your entire infrastructure
- Repeatable deployments across environments
- Automated testing of infrastructure changes
- Easy rollbacks when issues occur
- Documentation as code that stays current
FormKiQ stacks deploy via CloudFormation, integrating seamlessly with these IaC approaches. For LLM-integrated workloads specifically, IaC allows you to rapidly experiment with different model combinations, adjust token limits, and optimize costs without manual configuration.
Security and Authentication
Security and authentication are foundational pillars of any robust AWS Serverless or AWS AI Stack, especially when building serverless AI applications that interact with sensitive data and external model providers. By leveraging AWS Lambda and API Gateway, developers can implement secure authentication and authorization workflows that keep each app’s data separate and protected within a trusted AWS foundation.
For example: the application authentication process typically begins with verifying user credentials and issuing JSON Web Tokens (JWTs), which are then used to secure API requests throughout the application. API Gateway acts as the entry point for all web and API traffic, integrating seamlessly with Lambda functions to enforce authentication and authorization logic. This ensures that only authorized users can access specific resources, keeping your stack’s data isolated from unauthorized access and from other model providers. While machine-to-machine connectivity might use trusted IAM access or API keys, the workflow is similar.
To further enhance security, the AWS Serverless or AWS AI Stack supports custom domain names, which can be configured using AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) and
Route53. This not only provides a professional web presence but also enables secure HTTPS communication for all API requests. A domain-oriented architecture allows developers to modularly add or customize security features in a way that suits the structure and branding of the organization, making it easy to adapt to evolving requirements or integrate with other tools.
Infrastructure access management is handled through AWS IAM, giving developers fine-grained control over who can access which resources deployed within the stack. By defining roles and permissions, you can ensure that users and services only have the access they need—nothing more. This approach, combined with the event-driven and serverless nature of the stack, provides a secure, scalable, and flexible foundation for modern scalable architectures and AI apps.
Deployment and CI/CD Pipeline
Deploying an AWS Serverless or AI Stack is streamlined and efficient, thanks to IaC, using tools such as CloudFormation, CDK, Terraform, or the Serverless Framework. By using this approach, a blueprint for the stack’s configuration and resources is available; with a single command, developers can deploy all serverless services in the stack. This approach eliminates manual setup and ensures consistency across deployments.
The deployment process is further enhanced by integrating CI/CD tools like GitHub Actions. By setting up a workflow that triggers on code changes, developers can automate the entire pipeline: running tests, building the application, and deploying it directly to the AWS account. This not only accelerates development cycles but also reduces the risk of human error during deployment.
For teams with more complex requirements, other tools such as AWS CodePipeline and AWS CodeBuild can be used to create sophisticated CI/CD pipelines. These tools allow you to automate deployments across multiple environments—dev, staging, and production—ensuring that each environment is up-to-date and consistent with your latest codebase.
By adopting these deployment practices, developers can focus on building features and business logic, confident that their serverless services are reliably and repeatably deployed. The combination of IaC tooling , template and configuration files, and automated workflows provides a modern, scalable approach to managing the full stack lifecycle in AWS.
Monitoring and Optimization
Ensuring the performance and scalability of your AWS Serverless or AWS AI Stack requires robust monitoring and continuous optimization; unlike more traditional server-based deployments, serverless has more points of orchestration that require observability. AWS provides a suite of tools—such as CloudWatch, X-Ray, and CloudTrail—that give developers deep visibility into their serverless applications. These services allow you to track API requests, monitor Lambda function performance, and audit access to resources, making it easier to identify bottlenecks and optimize your code.
For AI applications that process large volumes of data or require real-time feedback, a serverless stack is equipped to support streaming responses. This capability enables your Lambda functions to handle and deliver data incrementally, improving responsiveness and user experience, especially in scenarios involving powerful LLM models or complex data processing.
AWS Lambda’s built-in support for concurrency and parallel processing allows your application to scale automatically, handling multiple requests simultaneously without manual intervention. Combined with the event-driven architecture of a serverless stack, this ensures that your serverless architecture and AI applications remain responsive and cost-effective, even under unpredictable workloads.
By leveraging these monitoring and optimization tools, developers can proactively address performance issues, fine-tune their serverless services, and ensure that their applications deliver a seamless experience to users. This approach is essential for building serverless applications that are not only scalable and efficient but also reliable and cost-effective in the long run.
Focus on What Matters: Your Business Logic
The core principle remains unchanged, but is more relevant than ever:
Leverage proven patterns instead of building infrastructure from scratch.
Serverless architectures have matured to the point where well-tested patterns exist for most common workflows. Open source frameworks and reference implementations provide battle-tested approaches:
These frameworks demonstrate how to properly architect LLM-integrated applications with error handling, fallback strategies, and cost controls. They show how to configure API Gateway effectively, and how to connect services for document processing pipelines.
Your engineering time is better spent on:
- Designing user experiences that create value
- Building business logic that differentiates your product
- Optimizing integrations, prompts, and models for your specific use cases
- Analyzing data to drive decisions
- Training team members on new capabilities
The Path Forward
The cloud is powerful and constantly evolving. LLM integration opens new possibilities. Architectural patterns are being established and refined by the community. Rather than rebuilding what others have already solved and documented, you can build on proven foundations.
Serverless stacks let you leverage collective expertise, deploy production-ready patterns quickly, and focus on what creates value for your customers. Whether you're building traditional web applications, processing documents at scale, or integrating language models into your workflows, serverless stacks provide tested architectural foundations, allowing you to focus your innovation where it matters most.
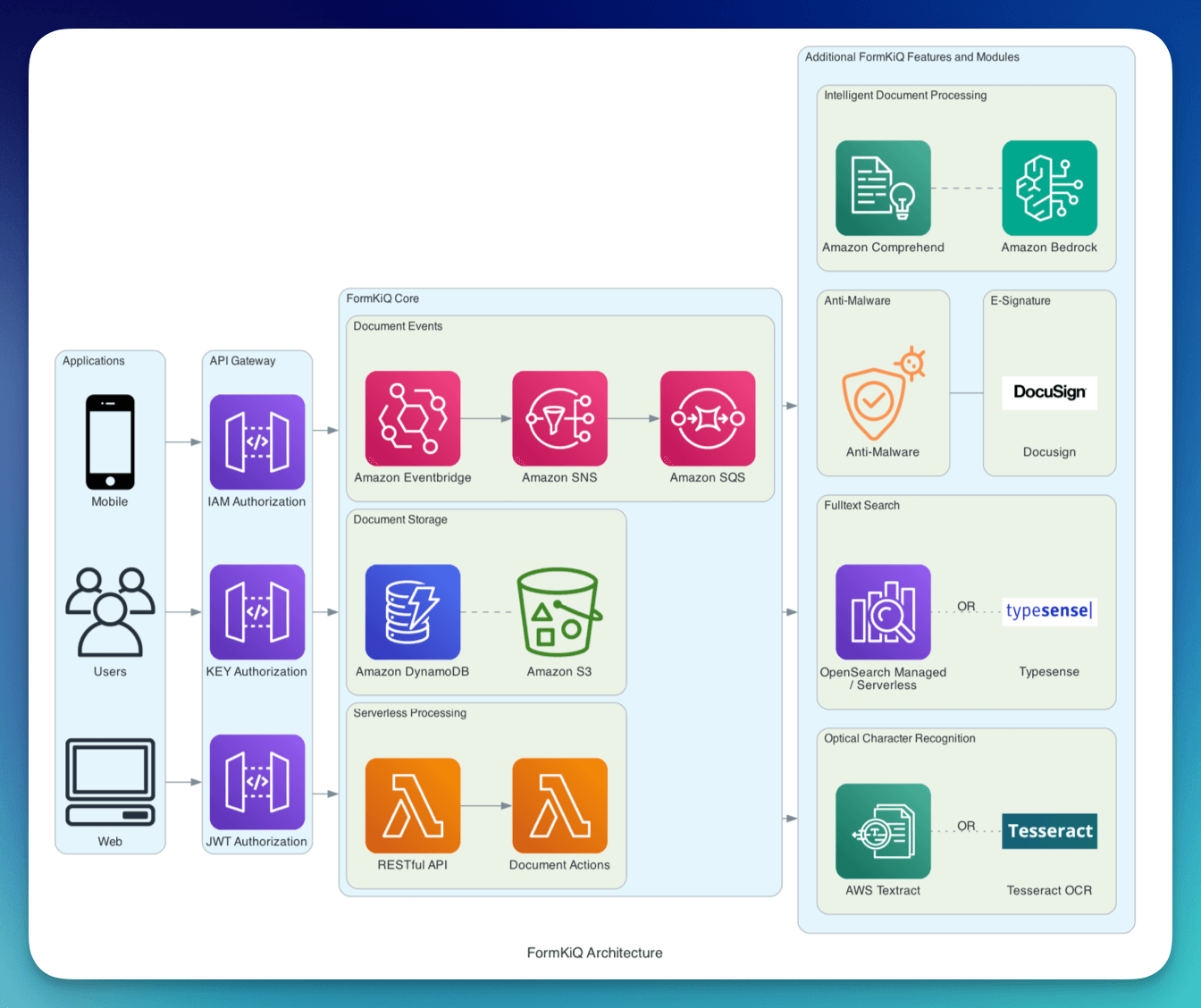
FormKiQ builds and maintains serverless document management stacks that integrate seamlessly with modern AI services, helping organizations focus on leveraging best-in-class document intelligence, rather than infrastructure management.
Contact us for more information on document processing, workflow automation, and information management.
 LATEST: The Complete Guide to Cloud Document Management: Why Architecture Matters Cloud-native vs. cloud-hosted: why architecture determines cost, compliance, and capabilities
LATEST: The Complete Guide to Cloud Document Management: Why Architecture Matters Cloud-native vs. cloud-hosted: why architecture determines cost, compliance, and capabilities FormKiQ vs. Off-the-Shelf Software and Less Flexible SaaS When is FormKiQ a better choice than Off-the-Shelf Software and Less Flexible SaaS?
FormKiQ vs. Off-the-Shelf Software and Less Flexible SaaS When is FormKiQ a better choice than Off-the-Shelf Software and Less Flexible SaaS? FormKiQ vs. Building It Yourself How does FormKiQ save time over custom in-house solutions?
FormKiQ vs. Building It Yourself How does FormKiQ save time over custom in-house solutions? Use Cases FormKiQ works for small and large workflows, across all verticals and industries.
Use Cases FormKiQ works for small and large workflows, across all verticals and industries. FormKiQ For Teams Find out how FormKiQ can work for your team
FormKiQ For Teams Find out how FormKiQ can work for your team FormKiQ For Industries Discover the advantages FormKiQ can bring to your industry
FormKiQ For Industries Discover the advantages FormKiQ can bring to your industry Blockchain and Decentralized Storage Leverage web3 technologies including proof of work and distributed systems for document control and data privacy
Blockchain and Decentralized Storage Leverage web3 technologies including proof of work and distributed systems for document control and data privacy Content and Digital Asset Management Integrate with your preferred web content management system while leveraging FormKiQ for managing your digital assets
Content and Digital Asset Management Integrate with your preferred web content management system while leveraging FormKiQ for managing your digital assets Document Management Module Integrate all of the required functionality of a document management system into an existing software solution
Document Management Module Integrate all of the required functionality of a document management system into an existing software solution Integration with QMS or LIMS Add missing functionality for your Quality Management or Laboratory Information Management by integrating with FormKiQ
Integration with QMS or LIMS Add missing functionality for your Quality Management or Laboratory Information Management by integrating with FormKiQ Job Application Form Receive applications, including cover letter and resume attachments, and import into an existing HR Management System
Job Application Form Receive applications, including cover letter and resume attachments, and import into an existing HR Management System Legal Discovery Tool Find information quickly by combining full-text search with AI-powered document classification
Legal Discovery Tool Find information quickly by combining full-text search with AI-powered document classification The Paperless Office: Digital Document Processing Collect, process, and store paper and digital documents, allowing for archival, integration, and future recall
The Paperless Office: Digital Document Processing Collect, process, and store paper and digital documents, allowing for archival, integration, and future recall Product Leasing System Process client lease applications, including a credit check and approval workflow
Product Leasing System Process client lease applications, including a credit check and approval workflow Company-Wide Break down the silos in your organization with a centralized control center for documents, ready for integration with any and all systems
Company-Wide Break down the silos in your organization with a centralized control center for documents, ready for integration with any and all systems Engineering and Product Reduce development time and agony with battle-tested components for your applications
Engineering and Product Reduce development time and agony with battle-tested components for your applications Finance and Accounting Process paper and electronic invoices and receipts, ready for integration with your important systems
Finance and Accounting Process paper and electronic invoices and receipts, ready for integration with your important systems HR and Recruiting Build and support your people across the organization by integrating with your essential tools
HR and Recruiting Build and support your people across the organization by integrating with your essential tools IT and InfoSec Provision a secure document store with the encryption and controls needed for compliance and protection
IT and InfoSec Provision a secure document store with the encryption and controls needed for compliance and protection Legal Manage and safeguard contracts and other essential documents across systems
Legal Manage and safeguard contracts and other essential documents across systems Marketing Add better discovery and reliability to digital assets and other essential content, while enabling integration with a web content management system
Marketing Add better discovery and reliability to digital assets and other essential content, while enabling integration with a web content management system Sales Keep track of sales assets and contracts inside and outside of your CRM and other tools
Sales Keep track of sales assets and contracts inside and outside of your CRM and other tools Accounting, Financial Services, and FinTech Standardize financial documents, metadata, and workflows across systems, teams, auditors, and clients
Accounting, Financial Services, and FinTech Standardize financial documents, metadata, and workflows across systems, teams, auditors, and clients Education, Training, and EdTech Integrate Learning Management Systems with other essential applications and tools
Education, Training, and EdTech Integrate Learning Management Systems with other essential applications and tools Healthcare, Life Sciences, and MedTech Combine secure and compliant records management with laboratory information management systems
Healthcare, Life Sciences, and MedTech Combine secure and compliant records management with laboratory information management systems Law Practices and Legal Services Ensure efficient legal discovery and case management
Law Practices and Legal Services Ensure efficient legal discovery and case management Logistics and Transportation Provide a robust and customized solution for fleet management or other logistics needs
Logistics and Transportation Provide a robust and customized solution for fleet management or other logistics needs Manufacturing, Production, and Utilities Control and distribute essential documents and standard operating procedures within and between facilities, partners, and clients
Manufacturing, Production, and Utilities Control and distribute essential documents and standard operating procedures within and between facilities, partners, and clients Online Entertainment, Gaming, and Gambling Provide the required compliance documents to partners, customers, and government agencies
Online Entertainment, Gaming, and Gambling Provide the required compliance documents to partners, customers, and government agencies Professional and Technical Services Ensure that clients, inspectors, and subcontractors are aligned with consistent document control
Professional and Technical Services Ensure that clients, inspectors, and subcontractors are aligned with consistent document control Tech Startups Build robust document management functionality into your disruptive product
Tech Startups Build robust document management functionality into your disruptive product